Smarter Automated Testing Strategies For Devs
#automated-testing-strategies#software-testing#CI/CD-integration#DevOps#quality-assurance
December 4, 2025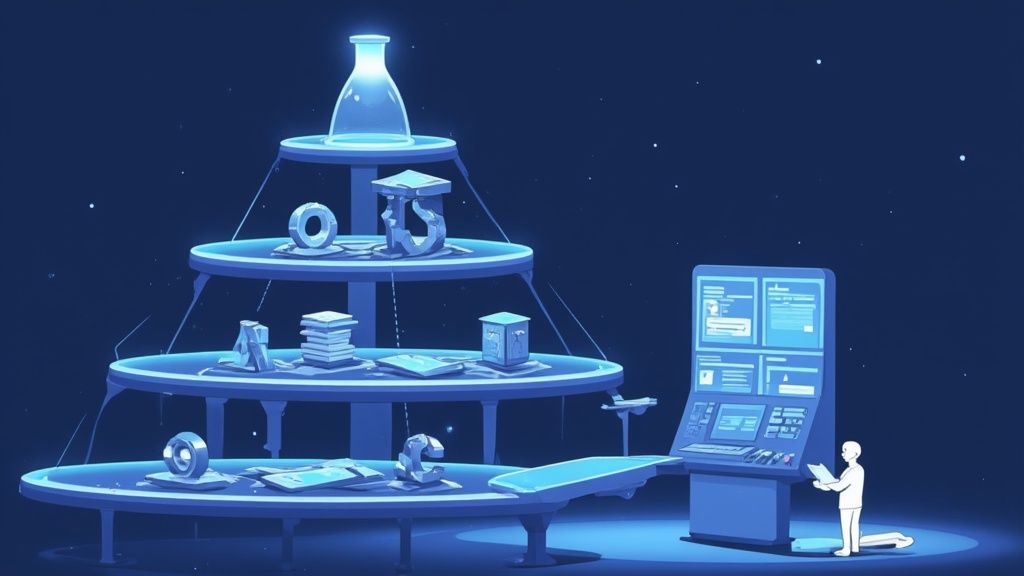
An automated testing strategy is your game plan for quality. It's a deliberate approach that outlines what to test, how to test it automatically, and when those tests should run throughout the development process. Think of it as the blueprint for quality assurance.
This blueprint ensures that every piece of your software - from the tiniest function to the full-blown application - is automatically validated before it ever gets near a customer. It transforms testing from a slow, manual bottleneck into a speedy, integrated part of how you build software.
Why Automated Testing Strategies Matter Now More Than Ever
In a world where speed is everything, manual testing just can't keep up. Every new feature, bug fix, or security patch brings the risk of breaking something that used to work perfectly. Having a human re-test the entire application after every small change is not just slow and expensive; it's a recipe for missed bugs and delayed releases.
This is where having a formal strategy becomes non-negotiable. It's not about just writing a bunch of test scripts. It's about making smart, intentional decisions to maximize the return on your automation investment.
A great automated testing strategy is like a modern car factory. Small, fast checks happen at every station - verifying the engine, the electronics, the chassis - long before the finished car gets a final inspection. This catches defects the moment they happen, preventing a costly and embarrassing recall down the road.
Balancing Speed with Uncompromising Quality
A well-crafted strategy directly tackles the classic business dilemma: how to deliver high-quality software without slowing down. It gives you a structured way to make sure you aren't trading stability for speed. The benefits are tangible and easy to see.
- Faster Release Cycles: When you automate the repetitive checks, you can test and deploy new code much more quickly.
- Greater Reliability: Automated tests are relentless. They run the same way every single time, catching regressions a human tester might overlook and leading to a more stable experience for your users.
- Reduced Long-Term Costs: It's always cheaper to find and fix a bug early in the development cycle than to deal with it after a customer finds it in production.
- Increased Developer Confidence: When developers trust that a solid suite of tests has their back, they feel more comfortable innovating and improving the codebase.
The Business Impact of Automated Testing
The move to automation isn't just a technical decision; it's a major business investment. The global automation testing market was valued at around USD 34.64 billion in 2024 and is expected to rocket to USD 197.12 billion by 2034. This explosive growth shows that companies no longer see automated testing as a "nice-to-have" but as essential infrastructure. You can explore more about these market trends to understand the drivers behind this shift.
At its core, a good strategy is about building a scalable system for ensuring quality. It frees up your team to focus on creating new features and value, not just putting out fires. This foundation is what allows us to build the robust testing frameworks we'll dive into next.
Before we move on, let's summarize the key pillars that make up a successful automated testing strategy.
Core Components of an Automated Testing Strategy
| Strategy Component | Objective | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Test Scope & Levels | Define what to test (unit, integration, E2E) and how much of each. | Focuses effort where it delivers the most value, preventing wasted time. |
| Tooling & Frameworks | Select the right tools for the job (e.g., Selenium, Cypress, Playwright). | Empowers teams with the technology needed to write effective and maintainable tests. |
| CI/CD Integration | Embed automated tests directly into the build and deployment pipeline. | Provides instant feedback to developers, catching bugs within minutes. |
| Test Data Management | Create a reliable and repeatable process for managing test data. | Ensures tests are consistent and not dependent on fragile, manual data setup. |
| Environment Strategy | Define where tests will run (local, staging, production-like). | Guarantees that tests are running in an environment that accurately reflects production. |
| Metrics & Reporting | Track key metrics like pass/fail rates, code coverage, and test flakiness. | Offers clear visibility into software quality and the effectiveness of the testing process. |
This table serves as a quick cheat sheet for the core ideas we'll be unpacking. Each component is a critical piece of the puzzle for building a quality-driven engineering culture.
Building a Solid Foundation with the Testing Pyramid
Every solid automated testing strategy needs a blueprint. Something that shows you how to balance different kinds of tests to get the most bang for your buck - maximum stability without killing your team's velocity. That blueprint is the Test Automation Pyramid. It's a simple but incredibly powerful model for structuring your test suite to catch bugs early and keep your pipeline flowing.
Think of it like building a house. You wouldn't just throw up all the walls and then check if the foundation is level. You inspect the quality at every single stage, starting from the ground up.
This is what a high-level strategic process looks like - it's about making conscious decisions about scope, timing, and tools before you ever write a single test.

This kind of structured thinking is exactly what the Testing Pyramid embodies. It gives you a framework for making those smart, deliberate choices.
The Base of the Pyramid: Unit Tests
The foundation of the pyramid - and by far the largest part of your test suite - is made of unit tests. These are small, lightning-fast tests that check a single "unit" of code in total isolation. A unit could be a function, a method, or a single component.
Going back to our house analogy, a unit test is like checking every single brick for cracks before it goes into a wall. You do thousands of these checks because they're cheap, they're fast, and they give you immediate feedback.
Unit tests are your first line of defense. They should run in milliseconds, execute every time code is saved, and tell a developer exactly what broke the moment a regression is introduced.
Because they're so quick and reliable, you should have tons of them. They form a wide, stable base that ensures all the fundamental building blocks of your application are solid before you even think about putting them together.
The Middle Layer: Integration Tests
Moving up a level, we get to integration tests. These tests are all about making sure different parts of your application play nicely together. They verify the connections between modules, the contract between your service and a database, or the handshake with an external API.
In our house build, an integration test is like making sure the plumbing fits correctly with the framing inside the walls. These tests are naturally more complex and slower than unit tests because they have to spin up multiple parts of the system. For instance, a test might check if your API can actually write data to a database and then successfully read it back out.
You'll have far fewer integration tests than unit tests. They cost more to write and maintain, and they take longer to run. Their job isn't to re-test the logic inside each component but to confirm that the seams between them are strong.
The Peak of the Pyramid: End-to-End Tests
Right at the top, we have End-to-End (E2E) tests. These are the big ones. They simulate a real user's journey through your application from start to finish, confirming the entire system works as a cohesive whole. A classic E2E test might involve automating a browser to log in, add a product to a cart, and go through the entire checkout process.
This is the final walkthrough of the finished house, where you flip all the light switches and turn on all the faucets. E2E tests give you the highest level of confidence, but that confidence comes at a steep price. They are, by a long shot, the slowest, most brittle, and most expensive tests in your arsenal.
Because of this, you should use them very sparingly. The pyramid's narrow peak is intentional - it reminds you to only cover your most critical, high-value user workflows with E2E tests, not every little feature.
Avoiding Common Anti-Patterns
One of the most common mistakes is to flip the pyramid on its head, creating what's known as the "Ice Cream Cone" anti-pattern. This is what happens when teams over-rely on slow, flaky E2E tests while neglecting the fast, reliable unit and integration tests.
This top-heavy approach creates a massive bottleneck. The test suite takes forever to run, fails for random reasons, and becomes a nightmare to maintain. A balanced strategy, guided by the pyramid, is your best defense against this and is key to shipping quality software at speed.
Expanding Your Toolkit with Modern Testing Patterns
The Test Pyramid gives us a fantastic blueprint for a balanced test suite, but modern applications are a different beast entirely. We're building systems with microservices, serverless functions, and a web of third-party integrations. These architectures introduce new failure points that your standard unit and integration tests just won't catch. To build a system that's truly resilient, you have to expand your toolkit with more specialized automated testing strategies.
Think of it like this: your pyramid tests are the foundational inspection of a new building. But now you need specialists to check the plumbing, electrical systems, and structural integrity under stress. Each of these modern test patterns serves a very specific purpose, creating a layered defense that catches bugs that would otherwise slip right into production. This ensures your application isn't just working, but is also fast, reliable, and secure.
Verifying Service Communication with API Testing
In today's world of distributed systems, applications rarely work in isolation. They're constantly talking to each other through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), the digital messengers that shuttle data between services. API testing cuts straight to this communication layer, completely bypassing the user interface.
Instead of writing a script that clicks buttons on a screen, an API test sends a request directly to a service endpoint and checks the response. Does it return the right data? The correct status code? This lets you confirm that your core business logic, data handling, and security rules are working as expected, all without the slow, brittle nature of a full UI test.
Think of API tests as calling a company's shipping department directly to check an order status, rather than navigating their customer service website. You get a faster, more direct answer about whether a critical process is working.
This approach is incredibly efficient, especially if you're working with microservices. You can quickly validate functionality, error handling, and performance for each individual service. If you're looking for the right tools to get started, you might want to check out some of the best API testing tools available today.
Enforcing Agreements with Contract Testing
API tests are great for proving a service works correctly on its own. But what happens when another team changes a service that your service depends on? This is where contract testing comes in. It solves the problem of keeping independently developed services in sync.
Contract tests create a formal agreement - a "contract" - between a service "consumer" and a "provider." The consumer defines exactly what it expects from the provider's API. The provider then uses this contract to run automated tests on their end, guaranteeing they never make a change that breaks their promise to the consumer.
- Consumer-Driven: The most common approach is for the service using the API (the consumer) to define the contract based on its needs.
- Provider Verification: The service providing the API then runs tests against this contract in its own CI/CD pipeline.
- Fail Fast, Fail Early: If the provider makes a change that violates the contract, their own build fails before they can deploy. This prevents a production outage that would have been incredibly difficult to track down.
This strategy is absolutely essential for maintaining stability in complex, distributed systems where multiple teams are shipping code independently.
Ensuring Scalability with Performance Testing
An application that works perfectly for one user but grinds to a halt under real-world traffic is a failure. Performance testing is a type of non-functional testing designed to see how your system behaves under pressure. The goal isn't to find functional bugs, but to uncover performance bottlenecks before your customers do.
There are a few key types of performance tests:
- Load Testing: This simulates your expected, everyday user traffic to see how the system holds up under normal conditions.
- Stress Testing: This pushes your system well beyond its expected limits to find its breaking point and see how it recovers.
- Spike Testing: This simulates a sudden, dramatic surge in traffic - like a Black Friday sale - to see if your system can handle the stampede.
Automating these tests in your CI/CD pipeline is a game-changer. It helps you catch performance regressions immediately, ensuring that a new feature doesn't accidentally bring the whole system down.
Protecting Your Assets with Security Testing
With security threats around every corner, you can't afford to treat security as an afterthought. Automated security testing bakes security checks directly into your development pipeline, a practice at the heart of DevSecOps. It involves using specialized tools to automatically scan your application for common vulnerabilities. Exploring the top security testing automation tools can give you a major head start.
This proactive approach to security includes several layers:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Scans your source code for potential security flaws before the application is even built.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Probes the running application from the outside, just like an attacker would, to find vulnerabilities.
- Dependency Scanning: Checks all your third-party libraries and packages for known security issues.
This "shift-left" philosophy makes finding and fixing vulnerabilities a normal, routine part of the development cycle, not a last-minute fire drill. This is especially critical in mobile, where a predicted compound annual growth rate of 25.3% in North America from 2025 to 2033 is driving a huge need for secure apps. Integrating security from day one is how you protect user data and build trust.
Integrating Testing into Your CI/CD Pipeline
Having an automated testing strategy is one thing, but making it a living, breathing part of your development process is where the magic happens. This is exactly where Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines come in. By weaving your tests directly into this automated workflow, you stop treating testing as a final hurdle and start making it an ongoing, integral part of how you build software.
The driving force behind this integration is the "Shift Left" philosophy. Think of your software development process as a timeline. It starts on the left with ideas and coding and ends on the right with deployment and production. For a long time, testing was a massive event that happened way over on the right, just before a release. Shifting left is all about moving those testing activities as early as humanly possible in that timeline.
This creates an incredibly powerful and immediate feedback loop for developers. Instead of finding out a change broke something days or even weeks later, they know within minutes. This proactive approach is the bedrock of modern automated testing strategies because it slashes the cost and complexity of fixing bugs.
Building Your Automated Quality Gates
You can think of a CI/CD pipeline as an automated assembly line for your code. At critical points along this line, you can install "quality gates" - specific test suites that must pass before any code can advance to the next stage. This setup automatically enforces a consistent quality standard for every single change.
Here's a common way to stage tests within a pipeline:
- On Every Commit: The moment a developer pushes a change, the pipeline kicks off the fastest tests. This is the perfect spot for unit tests, static analysis, and linting. Feedback is almost instant.
- On Every Pull Request: When a new feature is ready for peer review, a more substantial set of tests runs. This is where you'll typically execute your integration tests and API tests to make sure the new code plays nicely with the rest of the system.
- On Merge to Main/Staging: Once a pull request gets the green light and is merged, you can trigger an even broader suite. This might include a handful of critical end-to-end tests to validate key user journeys in a staging environment that mirrors production.
- Pre-Deployment: Right before you release to production, you can run final sanity checks. Think automated security scans or a quick smoke test against the live environment to ensure everything is configured and ready to go.
This tiered strategy strikes a great balance between speed and confidence. Developers get rapid feedback on small changes, while more exhaustive validation happens at logical checkpoints. As you hook your tests into your CI/CD pipeline, it's smart to explore integration options to ensure your tools connect smoothly with your existing systems.
Here's a look at how a CI/CD pipeline, such as one built with GitHub Actions, can bring these workflows to life.
This screenshot captures the essence of automation: build, test, and deployment workflows that turn simple code commits into tangible actions that automatically guard your quality.
From Pipeline to Production Confidence
By strategically placing different tests throughout your pipeline, you create a system that builds confidence at every step. Each successful stage gives your team more assurance that the code is stable, secure, and truly ready for users. This automated validation is the engine that powers fast, high-quality software delivery.
The goal of a CI/CD pipeline isn't just to automate deployment; it's to automate confidence. Every green checkmark should be a signal that your code is not only functionally correct but also meets your quality standards.
This level of automation also paves the way for more sophisticated release strategies. For example, once all your tests pass, the pipeline can automatically deploy new functionality behind feature flags. This lets you turn features on or off in production without a new deployment, giving you a fantastic safety net. If that's a new concept for you, our guide on how to implement feature flags is a great starting point.
By combining a robust CI/CD testing strategy with techniques like these, you can release changes much faster and with a whole lot less risk.
7. Solving Test Environment and Data Challenges
You can have the most brilliant automated tests in the world, but they're useless without a solid foundation to run on. I've seen countless promising automation strategies completely derailed by two classic roadblocks: shaky test environments and messy, unreliable test data.
Think about it. Your perfectly crafted script can't do its job if the server is down or the data it needs to verify is missing. The result is always the same: a failed test, a confused developer, and a colossal waste of time. Getting your environments and data right is the difference between a reliable automation suite and a constant source of flaky tests that erode everyone's trust.
Modernizing Test Environment Management
For years, the standard was a handful of shared, static testing servers. You know the ones - they probably had names like qa-server-01 or staging. These servers were a nightmare. They were configured manually, always in use, and perpetually out of sync with what was actually running in production.
This old way of working created massive bottlenecks. Teams would literally fight over server time, accidentally overwriting each other's deployments and causing tests to fail for reasons that had nothing to do with the code being tested. It was chaos.
The modern solution is to start treating your test environments just like you treat your application code. They should be something you can create, configure, and tear down on demand. This is the world of dynamic environments.
By using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation, you can spin up a pristine, production-like test environment for every single pull request. This approach completely eliminates the "it worked on my machine" problem and unlocks massive parallelization.
This on-demand model brings some serious advantages:
- Isolation: Every feature branch gets its own sandbox. No more stepping on each other's toes.
- Consistency: Since environments are built from code, you get a perfect mirror of your production setup every single time.
- Scalability: Need to run thousands of tests at once? Just spin up thousands of environments. Simple.
Mastering Test Data Management
Just as important as where you run your tests is the data you run them with. A test is only as good as the data it uses, and a mature strategy requires a dedicated practice for Test Data Management (TDM). Trust me, relying on a shared, fragile database is a recipe for disaster.
Instead, a solid TDM strategy uses a few key techniques to make sure tests are repeatable, reliable, and secure.
- Synthetic Data Generation: Instead of using real customer data, you can programmatically create realistic but fake data. This is fantastic for testing edge cases - like users with incredibly long names or weird addresses - that might not even exist in your live dataset.
- Data Masking and Anonymization: When you absolutely need data that looks and feels like production, you have to protect sensitive user information. Data masking tools automatically swap out real data (names, emails, credit card numbers) with plausible fakes, keeping you compliant with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Database Seeding: For every test run, you should automatically "seed" the database with the exact data that specific test needs. This makes tests completely self-contained and prevents them from being affected by whatever was left over from a previous run.
Pulling off these environment and data strategies requires deep expertise. It's why services have become such a huge part of the automation landscape, projected to hold 61% of the market revenue in 2025. Enterprises, which make up 69% of the market, often partner with specialists to build these tailored frameworks. You can discover more insights about automation testing services and see how they are shaping the industry.
Measuring the Success of Your Testing Strategy
So, you've put in the hard work to build an automated testing strategy. That's a huge win, but how do you know if it's actually paying off? Without measuring the impact, you're essentially flying blind. You need a data-driven approach to prove value, spot weaknesses, and figure out where to focus your energy next.
This isn't about creating pretty charts for a status report. It's about using metrics to tell a real story about quality. The right KPIs turn vague feelings like "I think things are better now" into concrete evidence, like "Our new API test suite cut production bugs by 30%."
Key Metrics That Tell a Story
To get a true picture of your testing health, you need to look past simple pass/fail numbers. A handful of core metrics can give you much deeper insight into what's really going on under the hood.
-
Test Pass Rate: This is the classic starting point - the percentage of tests that pass during a run. While a high rate is generally good, a constant 100% might be a red flag that your tests aren't challenging enough. On the other hand, a sudden drop is an immediate signal of a serious regression.
-
Flaky Test Percentage: A flaky test is one that passes and fails randomly, even when the code hasn't changed. These are poison to a CI/CD pipeline because they destroy developers' trust. Tracking this percentage helps you hunt down and fix these unreliable tests, making sure your test suite remains a credible source of truth.
-
Defect Escape Rate: This is the big one. It measures how many bugs slip through your safety net and are found by users in production. A low defect escape rate is the ultimate validation that your automated testing strategies are working as intended.
To keep things clear, here's a quick breakdown of the most important metrics you should be tracking.
Key Metrics for Automated Testing Success
| Metric/KPI | What It Measures | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Test Pass Rate | The percentage of tests that successfully pass in a given execution cycle. | Provides a high-level, immediate health check of the build. A sudden drop signals a major issue. |
| Flaky Test Percentage | The percentage of tests that produce inconsistent results (pass/fail) without code changes. | High flakiness erodes trust in the test suite and can lead to developers ignoring real failures. |
| Defect Escape Rate | The number of bugs discovered in production after a release has passed all tests. | This is the ultimate measure of quality effectiveness. A low rate means your tests are catching what they should. |
| Test Execution Time | The total time it takes for a test suite to run. | Long execution times slow down the feedback loop for developers, negating a key benefit of CI/CD. |
| Code Coverage | The percentage of your codebase that is executed by your automated tests. | Helps identify untested parts of your application, but should be used as a guide, not a strict goal. |
Tracking these KPIs consistently is what separates a good testing strategy from a great one. They give you the data needed to continually refine and improve your approach.
Using Data to Drive Decisions
Just tracking metrics isn't enough; you have to use that data to guide your decisions. For instance, if your Defect Escape Rate is creeping up, it might mean your integration test coverage is too thin. A high Flaky Test Percentage could point to instability in your test environment or problems with how you manage test data.
By spotting these trends, you can focus your improvement efforts where they'll have the most impact. For a much deeper exploration of this, our guide on how to measure software quality provides more advanced techniques.
Metrics are the language of business. They translate technical improvements into tangible outcomes like reduced customer support tickets, faster release cycles, and higher user satisfaction.
Ultimately, these numbers empower you to justify investments, whether it's for new tools or more training. They help you continuously tune your quality process, making your entire engineering organization more effective.
Common Questions About Automated Testing Strategies
When you first start building out an automated testing strategy, you're bound to run into a few common roadblocks and questions. It's a well-trodden path, and getting clear answers from those who have been there before can save you a lot of headaches.
Let's break down some of the most frequent questions teams ask. The goal here is to give you straightforward advice so you can make confident decisions as you build and scale your testing.
How Much Test Automation Is Enough?
It's tempting to aim for 100% automation, but in the real world, this is almost never a smart goal. It's not just impractical; it's often a waste of money. Chasing that magic number can push teams to spend time automating trivial tests while the tricky, high-value areas that need a human eye - like exploratory testing - get ignored.
Instead of fixating on a percentage, think in terms of risk. A much better approach is to automate your most critical user journeys and all of those repetitive regression checks. You've hit the sweet spot when your automated suite gives you rock-solid confidence in your core features. This frees up your manual testers to do what they do best: dig into complex scenarios and really validate the user experience.
The right amount of automation isn't a number. It's the point where you've covered your biggest risks for the lowest possible maintenance effort. Focus on automating the things that are critical, repetitive, and stable.
What Should We Automate First?
Getting started can feel like trying to boil the ocean. The secret is to prioritize what gives you the biggest bang for your buck, right from the start.
Here's a simple game plan:
- High-Traffic Features: Begin with the parts of your application that get the most user traffic. A bug here will impact the most people, so it's your biggest area of risk.
- Core Business Workflows: Think about the handful of things that absolutely must work - user registration, login, checkout. If these break, your business is in trouble. Automate them.
- The Most Tedious Manual Tests: Ask your QA team which tests are the most mind-numbingly repetitive and time-consuming. Automating these first gives them an immediate win and frees up their time for more valuable work.
By tackling these areas first, you'll see results quickly and build real momentum. It's the best way to prove the value of your testing strategy and get the buy-in you need to keep going.
At Pratt Solutions, we specialize in designing and implementing robust automation and CI/CD pipelines that accelerate development and enhance quality. If you're looking to build a scalable testing strategy, explore our custom cloud-based solutions and technical consulting services.